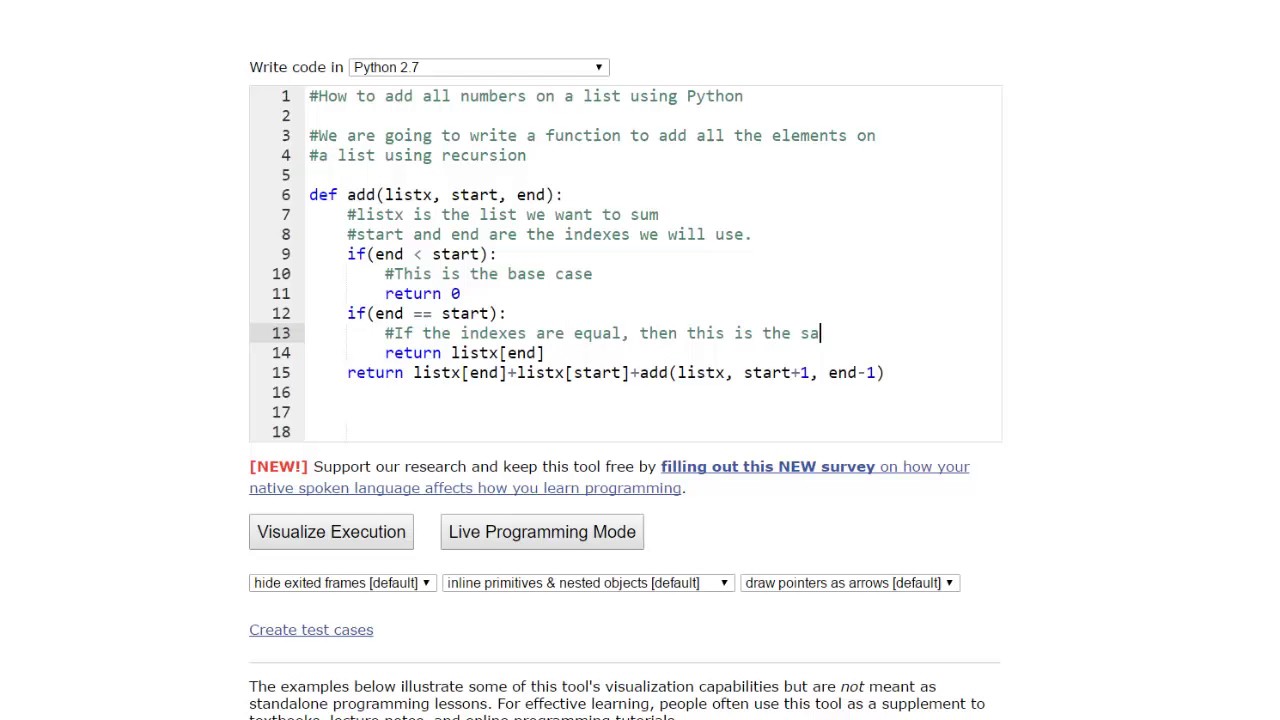
Above code defines a recursive method to calculate the sum of list items. It takes 2 arguments, the list whose elements need to be added and the size of list. When two lists are combined, a new list is created with each element equal to the sum of the items in the two lists' respective positions. Therefore, the sum of the integers in the list is needed.
The sum() method in Python computes the sum of all mathematical values in an iterable. Either integers and floating-point values can be added with sum(). A number can be added to the total using the sum() function's additional parameter. To find the average of a list, a list should be defined with a numerical set of values inside square brackets.
The average of lists can only be calculated on numerical values, not on string values. The average is the sum of elements divided by the number of elements. You can use the python built-in sum() function to get the sum of list elements.
Alternatively, you can use a loop to iterate through the list items and use a variable to keep track of the sum. Python sum () is an inbuilt function that takes an iterable and returns the sum of items in it. The sum () function adds the elements of an iterable and returns the sum.
Sum of numbers in the list is required everywhere. Python provides an inbuilt function sum () which sums up the numbers in the list. Hello everyone, am back to discuss about a new python program.
Here we learn how to sum all the elements in a list quite easily. We use a predefined function called sum() and apply it to the list, the functions returns the sum of all the elements in a list. ¶Return an iterator that applies function to every item of iterable, yielding the results. If additional iterable arguments are passed,function must take that many arguments and is applied to the items from all iterables in parallel.
With multiple iterables, the iterator stops when the shortest iterable is exhausted. For cases where the function inputs are already arranged into argument tuples, see itertools.starmap(). If the input list is empty, then the function returns 0. The for loop is the same one that you saw before. The sum () function adds start and elements of the given iterators from left to right.
The iterable may be Python list, tuple, set, or dictionary. To find a sum of the list in Python, use the sum () method. In this example, we have initialized the variable sum_num to zero and used for loop. The for-loop will loop through the elements present in the list, and each number is added and saved inside the sum_num variable. The average of list Python is calculated by using the sum_num divided by the count of the numbers in the list using len() built-in function.
Now, we have another simple example for you to work on. After that, a variable "total_m" will keep the value of the sum of total marks. You will observe that we have not stated any start parameter. If we will not specify any start value, you may consider it as "0".
Then, we have a print statement that will exhibit the end result on the output screen. When list size reaches 0 the last recursive call terminates by returning 0 and method returns the sum of list elements. Here, the list called numlistcontains integers as strings. Inside the forloop, these string elements are added together after converting them into integers, using the int() method. Internally, sum() adds start plus the values in iterable from left to right.
The values in the input iterable are normally numbers, but you can also use lists and tuples. The optional argument start can accept a number, list, or tuple, depending on what is passed to iterable. To find a sum of the list in Python, use the sum() method. You need to define the list and pass the list as a parameter to the sum() function, and in return, you will get the sum of list items.
Let's take a list and apply the sum function on it and see the result. In this method first, we are creating a variable total to store the sum and initializing it to 0. Next, the for loop iterates over each element of the array / list and storing their sum in the total variable, at last function returns the total.
In this program, we need to calculate the sum of all the elements of an array. This can be solved by looping through the array and add the value of the element in each iteration to variable sum. The average is calculated by using the sum_num divided by the count of the numbers in the list by using the len() built-in function. In Python, we can find the average of a list by simply using the sum() and len() function.
In this example, the sum() and len() built-in functions are used. It is a straightforward way to calculate the average as no loop is required to run through the elements, and also, the code size is reduced. The average can be calculated with just one line of code as shown below. This function accepts a list and a callback function as argument. Callback function will be our function that checks the condition.
This example will demonstrate where we will calculate the sum to get the average of the numbers. After that, a variable "s" will keep the value of the sum of total numbers in the list. You can confirm that we have not provided any start parameter. Returns the sum with a specified data type, using any of the input arguments in the previous syntaxes.
Outtype can be 'default', 'double', or 'native'. This post lists out various methods that can be utilized to calculate sum of list elements. In this program, elements of the numlistarray are added using a while loop.
The loop runs until the variable iis less than the length of the numlistarray. The final summation is printed using the value assigned in the totalsumvariable. In this article, we are going to calculate the sum of squares in python. We are going to learn different ways to calculate the sum of squares in python.
Using for loop, while loop, and using functions to calculate the sum of squares. At the end of the article, we will get a clear idea about this topic. Although this behavior can be useful, it is sometimes unexpected or undesirable. That's why Python is free to alias strings when it sees an opportunity to economize. The values that make up a list are called its elements, or its items. We will use the term element or item to mean the same thing.
Lists are similar to strings, which are ordered collections of characters, except that the elements of a list can be of any type. Lists and strings — and other collections that maintain the order of their items — are called sequences. Numpy library is a commonly used python library to work on large multi-dimensional arrays. It additionally has a huge assortment of numerical functions to be utilized on large arrays to perform different tasks. Numpy uses mean() function to calculate the average of the list.
For this, the mean is imported from the NumPy module. The list is one of Python's built-in Data types. It is a data type where data can be stored in a different form. The list uses square brackets with comma-separated values to store data. Data inside the lists can be of any type say, integer, string, or float value. String data should be in double quotes or single quotes.
Lists can be defined using any variable name and then assigning different values to the list in a square bracket. The given lambda function is applied to each element in the list and result is stored in the map object. As our lambda function returns a a bool, so map object contains bool elements. We can check the result by printing map object contents i.e. In this example the sum() and len() built-in functions are used to find average in Python. It is a straight forward way to calculate the average as you don't have to loop through the elements, and also, the code size is reduced.
In this post, you learned how to calculate the Python average of a list and of lists of lists. You learned how to do this with built-in functions including sum and len, as well as external packages including numpy and statistics. Finally, you learned how to calculate both row-wise and column-wise averages of lists of lists.
The sum() is a built-in Python function that takes an iterable as an argument, adds the elements of an iterable, and returns the sum. The iterators can be anything like List, Tuple, Set, or Dictionary. After the loop completes, variable in step 1 will be holding the sum of list elements. With zip(), you generate a list of tuples with the values from each of the input sequences. The generator expression loops over each tuple while multiplying the successive pairs of values previously arranged by zip().
The final step is to add the products together using sum(). So far, you've learned the basics of working with sum(). You've learned how to use this function to add numeric values together and also to concatenate sequences such as lists and tuples.
In all these examples, sum() computes the arithmetic sum of all the values in the input iterable regardless of their types. In the two dictionary examples, both calls to sum() return the sum of the keys of the input dictionary. The first example sums the keys by default and the second example sums the keys because of the .keys() call on the input dictionary.
A list comprehension is initially used to filter the list so that the elements that remain satisfy the condition. Subsequently, use the function sum() to add the remaining values. This article seeks to illustrate how to find the sum of the elements in a list provided these elements are numbers. There are various ways to sum a lists' elements in Python.
We hope that by the end of this article, you would have mastered at least one approach that resonates with you more. In Python programming, a list is created by placing all the items inside square brackets [] , separated by commas. It can have any number of items and they may be of different types (integer, float, string etc.). A list can also have another list as an item. By default this methods are considered as string, since input() method returs string. Use map() function to convert all elements as integer and store it in list.
The time complexity of the sum() function is linear in the number of elements in the iterable (list, tuple, set, etc.). The reason is that you need to go over all elements in the iterable and add them to a sum variable. Thus, you need to "touch" every iterable element once. A common error that arises while using the sum() function, is when the list contains a string.
Since it is not possible to add int values in strings, Python returns a TypeError. But the reduce function accepts any function as an argument that takes two arguments and returns a result. We can use the inbuilt reduce() function to reduce the loop and by using the lambda function, we can compute the summation of the list. For using the reduce function, reduce has to be imported from functools module. Map() Function in python accepts a function and an iterable like list.
Then applies the given function to each element in the list and appends the result of function in a new list. In the end map() returns this new list i.e. list of results. There are two optional keyword-only arguments. The key argument specifies a one-argument ordering function like that used for list.sort(). Thedefault argument specifies an object to return if the provided iterable is empty. If the iterable is empty and default is not provided, aValueError is raised.